Porteur de projet : Jérôme Lafont
Personnes impliquées dans le projet : F. Mallein-Gerin, M. Pasdeloup, Sherine Moustaghfir
![]()
Although many epigenetic modifications have been described during osteoarthritis (OA), the precise contribution of the chromatin remodeling enzymes during OA is still unclear. The histone demethylase LSD-1 (Lysine-Specific-Demethylase-1) is up-regulated in OA joints and induces the expression of inflammatory molecules such as mPges-1. We found that LSD1 downregulates the COL9A1 gene, which encodes a structural protein of the cartilage collagen fibrils (the type IX collagen) synthesised by articular chondrocytes. These results suggest that LSD1 plays an important role in articular cartilage, notably as a potential promoter of OA. Thus we study the LSD-1 mediated epigenetic signaling in the context of cartilage homeostasis and test the inhibition of LSD-1 as a strategy to prevent OA.
We use tamoxifen-inducible conditional knockout (cKO) mice to invalidate Lsd-1 specially in chondrocytes (Col2a1-CreERT: lsd-1fl/fl) to evaluate the impact of the absence of Lsd-1 on OA development. Various technics (IHC, FISH qPCR etc…) are used to characterise the joints and to evaluate the OA progression in post-traumatic OA (surgically-induced). The mechanisms (epigenetic signaling) by which catabolic/anabolic genes are regulated by LSD-1 are also investigated through in vitro approaches.
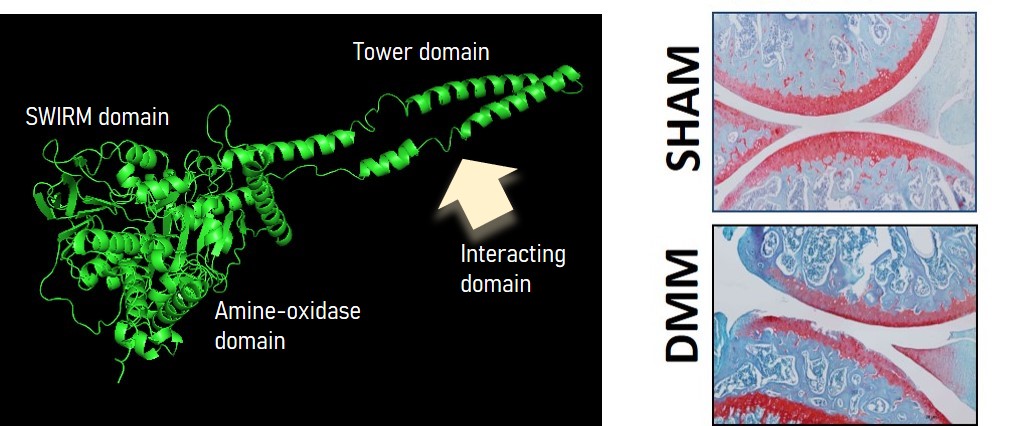
Left: structural analysis of LSD-1 (PyMol) highlights the potential site for protein-protein interactions (histone and non-histone). Right: safranin-O staining of knee joint section of sham vs. surgically-induced OA mice (DMM).
Sélection de publications :
1.
2. he Lysine Specific Demethylase-1 Negatively Regulates the COL9A1 Gene in Human Articular Chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6322. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176322. PMID: 32878268
3. Lafont JE, Poujade FA, Pasdeloup M, Neyret P, Mallein-Gerin F. (2016). Hypoxia potentiates the BMP-2 driven COL2A1 stimulation in human articular chondrocytes via p38 MAPK. Osteoarthritis & Cartilage. 2016 May ;24(5):856-67. doi : 10.1016/j.joca.2015.11.017.
4. Thoms BL, Dudek KA, Lafont JE and Murphy CL (2013). Hypoxia promotes production and inhibits destruction of human articular cartilage. Arthritis and Rheum. 2013 May 65(5)1302-12. doi : 10.1002/art.37867.
5. Dudek KA§, Lafont JE§, Martinez-Sanchez A, Murphy CL. (2010). Type II collagen expression is regulated by tissue-specific miR-675 in human articular chondrocytes.The Journal of Biol. Chem. 285 (32) : 24381-7. doi : 10.1074/jbc.M110.111328.
Article recommandé dans![]()
6. Murphy CL, BL Thoms, RJ Vaghjiani and JE Lafont (2009). HIF-mediated articular chondrocyte function: prospects for cartilage repair.Arth. Res. and Ther. 11(1):213
7. Lafont JE, Talma S, Hopfgarten C, Murphy CL (2008). Hypoxia promotes the differentiated human articular chondrocyte phenotype through SOX9-dependent and -independent pathways.The Journal of Biol. Chem. 283 (8) 4778-4786.
Collaborations :
Pr. M. Cohen Solal, Laboratoire Bioscar (Inserm U1132), Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris
Pr. S. Lustig and E. Servien, Hôpital de la Croix-rousse, Lyon



